GIS in Water Resources: Lecture 1
GIS in Water Resources: Lecture 1. In-class and distance learning Geospatial database of hydrologic features GIS and HIS Curved earth and a flat map. Lectures Powerpoint slides Video streaming Readings “Arc Hydro: GIS in Water Resources” and other materials Homework Computer exercises
Share Presentation
Embed Code
Link
Download Presentation
- data
- arc hydro
- data model
- hydrologic data
- synthesizing hydrologic data
- cuahsi water data services

merrill-donaldson + Follow
Download Presentation
GIS in Water Resources: Lecture 1
An Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only. Download presentation by click this link. While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server. During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.
Presentation Transcript
- GIS in Water Resources: Lecture 1 • In-class and distance learning • Geospatial database of hydrologic features • GIS and HIS • Curved earth and a flat map
- Lectures Powerpoint slides Video streaming Readings “Arc Hydro: GIS in Water Resources” and other materials Homework Computer exercises Hand exercises Term Project Oral presentation HTML report Class Interaction Email Discussion Examinations Midterm, final Six Basic Course Elements
- Dr David Tarboton Students at Utah State University Dr Ayse Irmak Students at University of Nebraska - Lincoln Our Classroom Dr David Maidment Students at UT Austin
- Traditional Classroom Community Inside and Outside The Classroom University Without Walls
- Instructor-Centered Presentation Community-Centered Presentation Learning Styles Instructor Student We learn from the instructors and each other
- GIS in Water Resources: Lecture 1 • In-class and distance learning • Geospatial database of hydrologic features • GIS and HIS • Curved earth and a flat map
- Geographic Data Model • Conceptual Model – a set of concepts that describe a subject and allow reasoning about it • Mathematical Model – a conceptual model expressed in symbols and equations • Data Model – a conceptual model expressed in a data structure (e.g. ascii files, Excel tables, …..) • Geographic Data Model – a conceptual model for describing and reasoning about the world expressed in a GIS database
- Data Model based on Inventory of data layers
- Spatial Data: Vector format Vector data are defined spatially: (x1,y1) Point - a pair of x and y coordinates vertex Line - a sequence of points Node Polygon - a closed set of lines
- Themes or Data Layers Vector data: point, line or polygon features
- Kissimmee watershed, Florida Themes
- Attributes of a Selected Feature
- Raster and Vector Data Raster data are described by a cell grid, one value per cell Vector Raster Point Line Zone of cells Polygon
- Santa Barbara, California http://srtm.usgs.gov/srtmimagegallery/index.html
- How do we combine these data? Digital Elevation Models Streams Watersheds Waterbodies
- An integrated raster-vector database
- Point Water Observations Time Series A point location in space A series of values in time
- Linking Geographic Information Systems and Water Resources Water Resources GIS
- Water Information in Space and Time
- GIS in Water Resources: Lecture 1 • In-class and distance learning • Geospatial database of hydrologic features • GIS and HIS • Curved earth and a flat map
- What is CUAHSI? UCAR • CUAHSI –Consortium of Universities for the Advancement of Hydrologic Science, Inc • Formed in 2001 as a legal entity • Program office in Washington (5 staff) • NSF supports CUAHSI to develop infrastructure and services to advance hydrologic science in US universities Unidata Atmospheric Sciences Earth Sciences Ocean Sciences CUAHSI National Science Foundation Geosciences Directorate HIS
- CUAHSI Member Institutions 122 Universities as of August 2009
- Hydrologic Information System Goals • Data Access– providing better access to a large volume of high quality hydrologic data; • Hydrologic Observatories– storing and synthesizing hydrologic data for a region; • Hydrologic Science– providing a stronger hydrologic information infrastructure; • Hydrologic Education– bringing more hydrologic data into the classroom.
- Water Data Water quantity and quality Soil water Rainfall & Snow Modeling Meteorology Remote sensing
- Data are Published in Many Formats
- Services-Oriented Architecture A services‐oriented architecture is a concept that applies to large, distributed information systems that have many owners, are complex and heterogeneous, and have considerable legacies from the way their various components have developed in the past (Josuttis, 2007).
- HTML as a Web Language Text and Pictures in Web Browser HyperText Markup Language Vermont EPSCoR-->
- WaterML as a Web Language Discharge of the San Marcos River at Luling, TX June 28 - July 18, 2002 USGS Streamflow data in WaterML WaterML is constructed as a Web Services Definition Language using WWW standards
- CUAHSI Water Data Services 35 services 15,000 variables 1.75 million sites 8.33 million series 342 million data
- Texas Water Data Services 10 services 7,010 variables 15,870 sites 645,566 series 23,272,357records
- A Theme Layer Synthesis over all data sources of observations of a particular variable e.g. Salinity
- Arc Hydro An ArcGIS data model for water resources Arc Hydro toolset for implementation Framework for linking hydrologic simulation models Arc Hydro: GIS for Water Resources The Arc Hydro data model and application tools are in the public domain
- Arc Hydro—Hydrography The blue lines on maps
- Arc Hydro—Hydrology The movement of water through the hydrologic system
- Integrating Data Inventory using a Behavioral Model Relationships between objects linked by tracing path of water movement
- Drainage System Hydro Network Flow Time Time Series Hydrography Channel System Arc Hydro Components
- Analysis, Modeling, Decision Making Arc Hydro Geodatabase Hydrologic Information System A synthesis of geospatial and temporal data supporting hydrologic analysis and modeling
- GIS in Water Resources: Lecture 1 • In-class and distance learning • Geospatial database of hydrologic features • GIS and HIS • Curved earth and a flat map
- Origin of Geographic Coordinates Equator (0,0) Prime Meridian
- Latitude and Longitude Longitude line (Meridian) N W E S Range: 180ºW - 0º - 180ºE Latitude line (Parallel) N W E S (0ºN, 0ºE) Equator, Prime Meridian Range: 90ºS - 0º - 90ºN
- 60 N 30 N 60 W 120 W 90 W 0 N Latitude and Longitude in North America 40 50 59 96 45 0 Austin: Logan: Lincoln: (30°18' 22" N, 97°45' 3" W) (41°44' 24" N, 111°50' 9" W) (40°50' 59" N, 96°45' 0" W)
- Map Projection Flat Map Cartesian coordinates: x,y (Easting & Northing) Curved Earth Geographic coordinates: f, l (Latitude & Longitude)
- Representative Fraction Globe distanceEarth distance = Earth to Globe to Map Map Projection: Map Scale: Scale Factor Map distanceGlobe distance = (e.g. 0.9996) (e.g. 1:24,000)
- Coordinate Systems A planar coordinate system is defined by a pair of orthogonal (x,y) axes drawn through an origin Y X Origin (xo,yo) (fo,lo)
- Summary (1) • GIS in Water Resources is about empowerment through use of information technology – helping you to understand the world around you and to investigate problems of interest to you • This is an “open class” in every sense where we learn from one another as well as from the instructors
- Summary (2) • GIS offers a structured information model for working with geospatial data that describe the “water environment” (watersheds, streams, lakes, land use, ….) • Water resources also needs observations and modeling to describe “the water” (discharge, water quality, water level, precipitation)
- Summary (3) • Geography “brings things together” through georeferencing on the earth’s surface • Understanding geolocation on the earth and working with geospatial coordinate systems is fundamental to this field

Lecture 24
Lecture 24. Biology 1108 Chapter 44: Control of the Internal Environment. Learning Objectives (1 of 3). Contrast Osmoregulation in salt water & fresh water fish Ectotherms and endotherms Define Homeostasis Discuss “Goose bumps”. Learning Objectives (2 of 3). Contrast:
1.02k views • 39 slides

Lecture 3 Internal Analysis: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive Advantage
BA 951 Policy Formulation and Administration. Lecture 3 Internal Analysis: Resources, Capabilities, Competencies, and Competitive Advantage. Learning Outcomes. A systematic look inside the firm – why are some firms more successful than others? The basis of competitive advantage
1.86k views • 29 slides

Arc Hydro: GIS for Water Resources
Arc Hydro Hydronetwork Drainage systems Channels Time Series Modeling Hydrologic integration. Arc Hydro: GIS for Water Resources. David R. Maidment, University of Texas at Austin. The Arc Hydro data model and application tools are in the public domain.
1.9k views • 64 slides
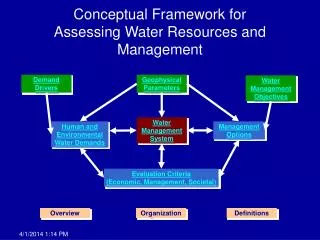
Conceptual Framework for Assessing Water Resources and Management
Conceptual Framework for Assessing Water Resources and Management. Demand Drivers. Geophysical Parameters. Water Management Objectives. Water Management System. Human and Environmental Water Demands. Management Options. Evaluation Criteria (Economic, Management, Societal). Overview.
1.85k views • 85 slides

Coagulation and Flocculation at Water Treatment Plants
Coagulation and Flocculation at Water Treatment Plants. WQT 131 Water Works Operation III Water Treatment Chapter 4 Coagulation and Flocculation Lecture 3. Week 3 Objectives . Reading assignment:
4.93k views • 51 slides

Chapter 11 WATER
Chapter 11 WATER. Mr. Manskopf Notes can also be found at http://www.manskopf.com. How many bodies of water can you identify/locate? Is there more or less water on Earth today then there was 1 billion years ago?. Goals for Chapter 11…. Describe where Earth’s water resources are located.
1.72k views • 86 slides

Water Resources
Water Resources. Chapter 13. Core Case Study: Water Conflicts in the Middle East: A Preview of the Future. Water shortages in the Middle East: hydrological poverty Nile River: flows through 7 countries, Ethopia @ the end is most desperate Jordan Basin: Tigris and Euphrates Rivers.
1.45k views • 98 slides

Water Resources and Water Pollution
Water Resources and Water Pollution. Chapter 11. Section 11-1. WILL WE HAVE ENOUGH USABLE WATER? . Freshwater is an irreplaceable resource that we are managing poorly. Freshwater is relatively pure and contains few dissolved salts.
1.57k views • 121 slides

Properties of Water
Properties of Water. Primarily due to polarity. Video1 “Properties of water” – 4 ½ min Why is ice less dense than water? How does ice floating on water impact the survival of the living organisms Draw the water structure. How does the term “polar” describe the water molecule?
1.22k views • 75 slides

Facing Climate Changes: Towards Sustainable Planning and Management of Water Resources Prof. Ezio Todini
Facing Climate Changes: Towards Sustainable Planning and Management of Water Resources Prof. Ezio Todini. Main changes of Water Resources availability during the twentieth century
945 views • 78 slides

Clean Water Act
Clean Water Act. Master Water Steward February 25, 2014 Faye Sleeper, Co-Director Water Resources Center. Clean Water Act Overview. Clean Water Act Overview Local and State governance Articles and discussion. Clean Water Act Context: Environmental Conditions.
1.45k views • 52 slides

Water Resources and Water Pollution
Water Resources and Water Pollution. Chapter 11. Section 11-1. WILL WE HAVE ENOUGH USABLE WATER? . Where is the water?. Freshwater is an irreplaceable resource that we are managing poorly. A person could survive for only a few days without water. Functions or Services of Water .
1.83k views • 70 slides

Hard Water & Soft Water
Hard Water & Soft Water. First Things First. What is Water Hardness ?. Hard water. Groundwater dissolves rocks and minerals releasing calcium, magnesium, and other ions that cause water to be hard. These dissolved ions give hard water its characteristics. Hard water.
8.99k views • 25 slides

An Overview of Water Resources Management in IR of Iran
In The Name Of God. An Overview of Water Resources Management in IR of Iran. Water & Wastewater Micro Planning Bureau Ministry of Energy 2012. Contents. 1. Water Resources Potentials and Related Issues 2. Development Procedure of Water Sector
1.67k views • 50 slides

Water Resources Development and Management Optimization (Linear Programming)
Water Resources Development and Management Optimization (Linear Programming). CVEN 5393 Mar 4, 2011. Acknowledgements Dr. Yicheng Wang (Visiting Researcher, CADSWES during Fall 2009 – early Spring 2010) for slides from his Optimization course during Fall 2009
1.05k views • 79 slides

6.096 Lecture 10
6.096 Lecture 10. Evolution Gene correspondence - Rearrangements - Genome duplication. 6.096 – Algorithms for Computational Biology – Lecture 9. Evolutionary change. Lecture 1 - Introduction Lecture 2 - Hashing / BLAST Lecture 3 - Combinatorial Motif Finding
2.23k views • 155 slides

ERT 246 HYDROLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING
ERT 246 HYDROLOGY AND WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING. Ms Siti Kamariah Bt Md Sa’at School of Bioprocess Engineering sitikamariah@unimap.edu.my. Text Book. Bedient B. P; Huber W.C and Vieux B.E,. (2008) Hydrology & Floodplain Analysis , 4th Ed. Prentice-Hall, Inc, Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458.
1.27k views • 66 slides
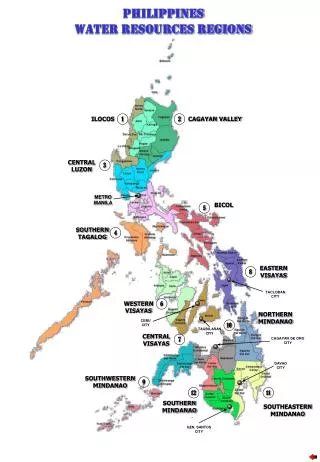
PHILIPPINES WATER RESOURCES REGIONS
PHILIPPINES WATER RESOURCES REGIONS. ILOCOS. CAGAYAN VALLEY. 1. 2. CENTRAL LUZON. 3. METRO MANILA. BICOL. 5. SOUTHERN TAGALOG. 4. EASTERN VISAYAS. 8. TACLOBAN CITY. WESTERN VISAYAS. 6. NORTHERN MINDANAO. CEBU CITY. 10. TAGBILARAN CITY. CENTRAL VISAYAS. 7.
3.37k views • 3 slides

Today’s Agenda: Lecture I
Today’s Agenda: Lecture I. Journal Questions: Describe three characteristics of water. What is the water cycle? *1. Lecture: The Water Cycle 2. Homework: Read water related chapter in your textbook. Nutrient Cycles: The Water (Hydrologic) Cycle. By Dr. Woodward. Nutrient Cycles.
1.8k views • 162 slides

Cold atoms
Cold atoms. Lecture 7. 21 st February, 2007. Preliminary plan/reality in the fall term. Lecture 1 … Lecture 2 … Lecture 3 … Lecture 4 … Lecture 5 … Lecture 6 … Lecture 7 …. Something about everything (see next slide) The textbook version of BEC in extended systems
2.15k views • 120 slides

Environmental Engineering Management (EEM 690)
Lecture 5. - Water Quality and IWRM - Soil and groundwater pollution and control. Environmental Engineering Management (EEM 690). FAISAL ANWAR. Water Quality Management: Rules and Regulations. Drinking Water: Australian Drinking Water Quality Guideline or WHO guideline
1.33k views • 85 slides

NWRMP: The Role of Stakeholders in Implementing the National Water Resources Master Plan
NWRMP: The Role of Stakeholders in Implementing the National Water Resources Master Plan. Dr. Martin O. Eduvie Coordinator/Project Manager RWSSC National Water Resources Institute Kaduna. What is NWRMP?. Nigeria Water Resources Master Plan: IWRM In Nigeria, we have challenges
1.5k views • 117 slides
























